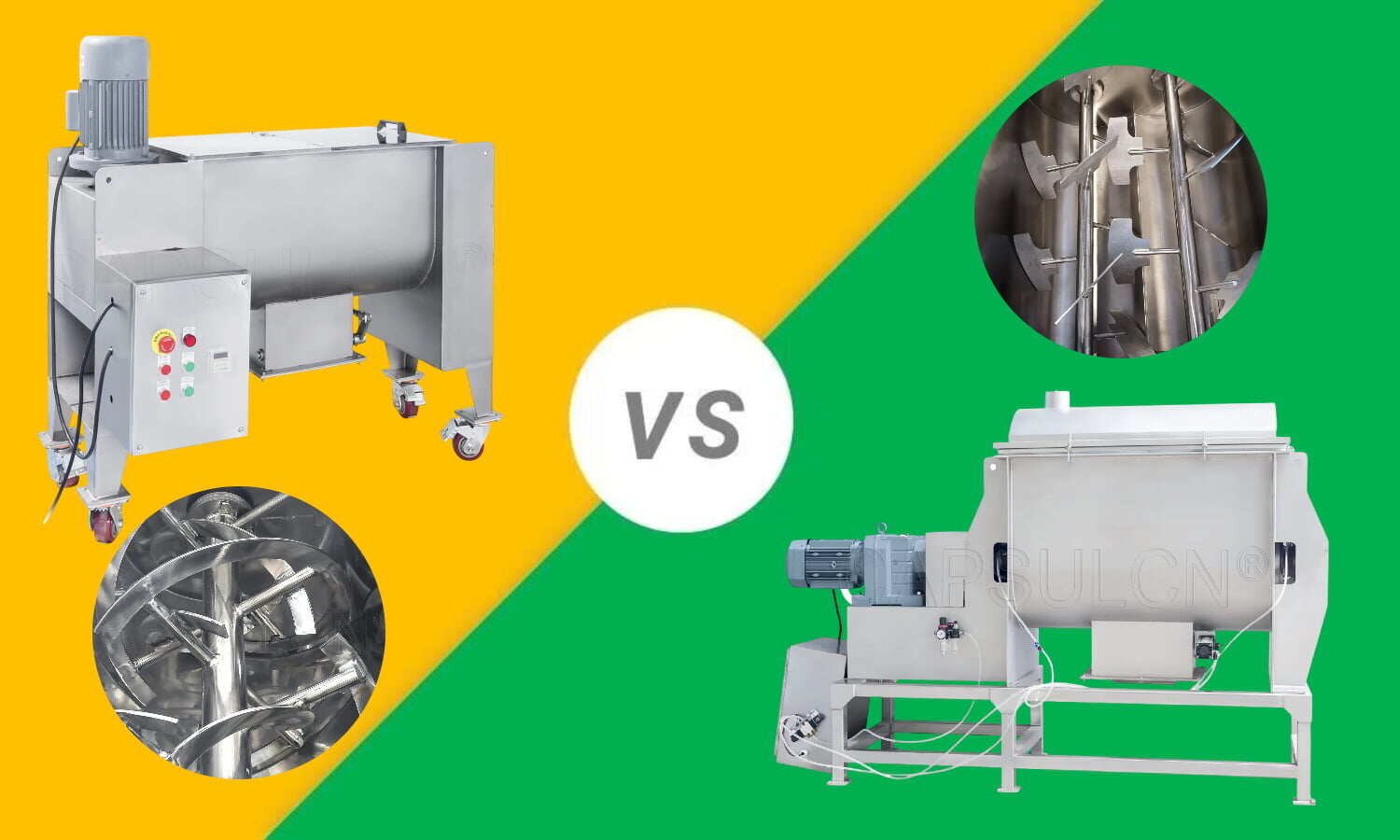

Are you looking for an efficient way to achieve a uniform material mix? Blending equipment is the answer! However, there are diverse types of blenders; choosing one that perfectly fits your mixing needs can't be that easy. No worries. This article has got you covered.
After doing some research, we've found that two of the most popular choices are ribbon blenders and paddle blenders. In this article, we'll break down their workings, pros and cons, and typical applications. All this information will help you better understand the differences between these two machines and make the right choice.
Ribbon Blender vs Paddle Blender: Definition
What is a Ribbon Blender?
A ribbon blender is an industrial mixing machine capable of handling both small and large-scale operations. It's typically used to blend dry, free-flowing solid forms. It can also deal with dry ingredients with small amounts of liquids.
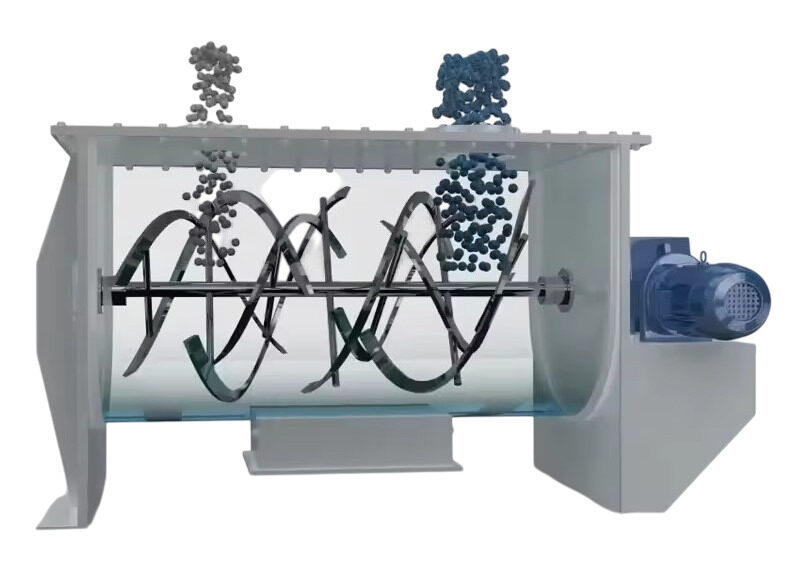
Ribbon blenders typically feature a horizontal agitator housed in a U-shaped trough. Inside, there is a long shaft running through the middle. Attached to this shaft are metal ribbons shaped like spirals—both inner and outer ribbons.
When the shaft rotates, these ribbons move the material in opposite directions. They act like blades to break lumps, if any. The ribbon agitator folds and lifts the content to mix it thoroughly.
What is a Paddle Blender?
A paddle blender has the same kind of U-shaped mixing chamber, but it works a bit differently. Instead of ribbons, it features flat or slightly curved paddles attached to the central shaft inside the trough.
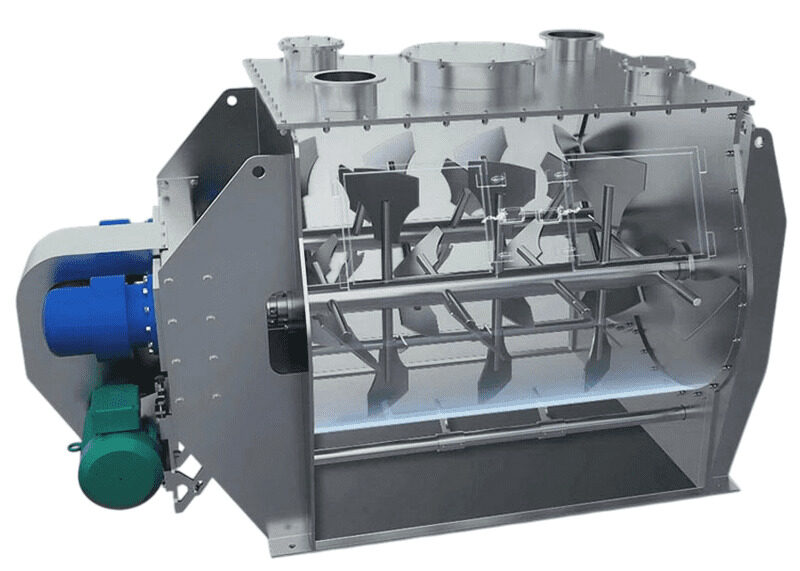

As the shaft turns, the paddles gently lift and flip the materials, creating a tumbling motion. This method is ideal for mixing fragile or delicate ingredients because it's less aggressive. Think of it like gently tossing a salad so you don't bruise the ingredients.
Ribbon Blender vs Paddle Blender: Workings
How Does a Ribbon Blender Work?
First off, let's take a look at the key components a ribbon blender has.
- U-shaped Trough: A spacious chamber where all the ingredients are placed and mixed.
- Central Shaft: A horizontal shaft running through the middle of the trough.
- Ribbon Agitators: Metal, helical ribbons attached to the shaft.
- Motor and Drive System: Powers the rotation of the shaft and ribbons.
- Discharge Valve: Allows the blended material to be emptied from the trough.
Working Principle (Step-by-Step):
- Place the materials into the U-shaped trough from the top.
- Start the motor to power the central horizontal shaft.
- The inner and outer helical ribbons attached to the shaft rotate. The outer ribbon pushes materials from the ends toward the middle. Meanwhile, the inner ribbon does the opposite.
- The ribbons lift, fold, and circulate the materials throughout the trough.
- Keep blending until a homogeneous mixture forms.
- Open the discharge valve at the bottom of the trough to let out the mixture.
How Does a Paddle Blender Work?
Let's check out some of the key components of a paddle blender:
- U-shaped trough: Just like the ribbon blender, it offers space for holding and mixing materials.
- Central Shaft: Runs horizontally through the trough.
- Paddles: Flat or slightly curved paddles of different sizes attached to the shaft at different angles.
- Motor and Drive System: Powers the rotation of the shaft and paddles.
- Discharge Valve: Allows for easy emptying of the mixed product.
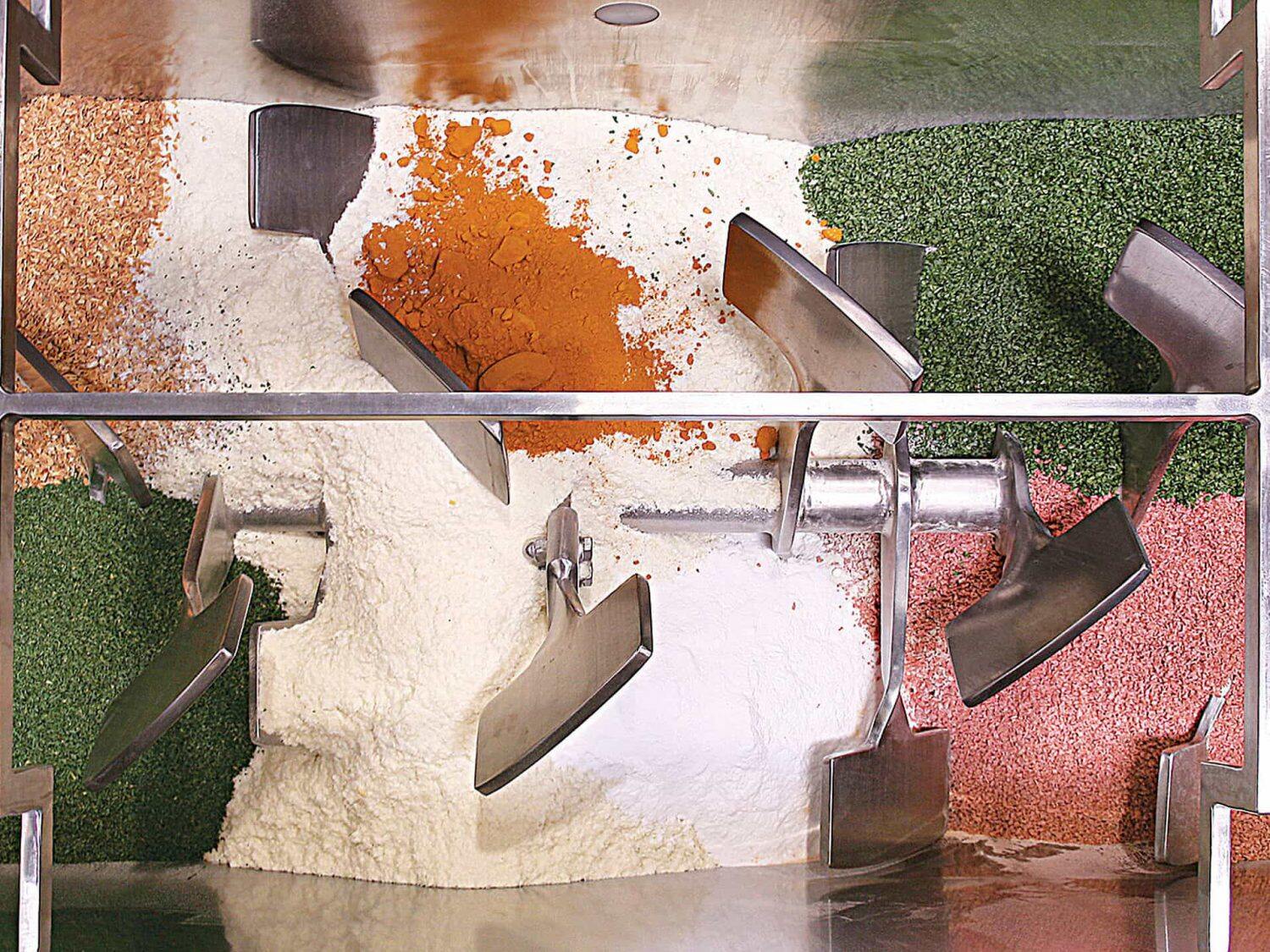

(Image Source: Eirich Machines)
Working Principle (Step-by-Step):
- Add materials or mixtures requiring liquids into the U-shaped trough.
- Activate the motor to drive the central horizontal shaft.
- Paddles rotate along with the shaft.
- Lift materials from the bottom and allow them to cascade back down.
- Incorporate liquids during mixing (if applicable).
- Continue the gentle tumbling and mixing until a homogeneous blend is reached.
- Release the blended product from the discharge valve.
Ribbon Blender vs Paddle Blender: Typical Applications
What are the Common Uses of Ribbon Blenders?
- Dry Solid-Solid Mixing:
- Food Industry: Blending flour, spices, baking mixes, powdered milk, and other dry ingredients.
- Pharmaceuticals: Mixing active ingredients with excipients to produce tablets and capsules.
- Chemicals: Combining dry chemicals for products like detergents, fertilizers, and plastics.
- Cosmetics: Preparing powdered makeup products such as foundations and eyeshadows.
- Homogeneous Blending of Free-Flowing Materials:
- Ideal for creating uniform mixtures where the ingredients have similar particle sizes and densities.
- Bulk Material Processing:
- Efficiently handles large volumes, making it suitable for high-capacity production environments.
- Minor Liquid Incorporation:
- Can mix small amounts of liquids into dry mixes without causing clumping.
What are the Common Uses of Paddle Blenders?
- Gentle Mixing of Fragile Ingredients:
- Food Industry: Mixing nuts, cereals, dried fruits, and other delicate items without breaking them.
- Pharmaceuticals: Blending sensitive compounds that high shear forces could damage.
- Animal Feed and Pet Food: Combining ingredients while maintaining the integrity of the components.
- Wet and Dry Mixing:
- Food Products: Incorporating liquids into dry mixes to create doughs, batters, or coatings.
- Chemical Processing: Mixing powders with liquids to form slurries or pastes.
- Heat-Sensitive Material Handling:
- Suitable for ingredients that may degrade or alter under the heat generated by more aggressive mixing.
- Sticky or Cohesive Materials:
- Effective in blending materials that tend to clump, as the gentle action reduces compaction.
Ribbon Blender vs Paddle Blender: Advantages and Limitations
Pros of Ribbon Blenders:
- Capable of handling various dry ingredients like powders, granules, and pellets.
- Available in different sizes, suitable for both small batches and large-scale production.
- The inner and outer ribbons create a unique counter-flow movement to ensure quick and thorough blending.
- Generally uses less energy for dry blending applications.
- Often less expensive than more complex mixing equipment.
- Straightforward to operate and maintain due to its uncomplicated structure.
Cons of Ribbon Blenders:
- Not ideal for fragile or brittle materials due to the high shear forces.
- Less effective when significant amounts of liquids need to be incorporated into the mix.
- Improper loading or design flaws can lead to dead spots.
- The intricate ribbon structure can make cleaning and sanitation more time-consuming.
Pros of Paddle Blenders:
- Can mix ingredients of different sizes, shapes, and densities, including sticky or cohesive substances.
- Achieves homogeneity even with challenging materials.
- Ideal for delicate or friable materials thanks to low-shear tumble action.
- Preserves the shape and texture of the ingredients.
- Excels at evenly distributing liquids into solids, suitable for creating doughs, slurries, or pastes.
- Gentle folding action helps prevent lumps and clumps in the mixture.
- The less complex structure makes cleaning and maintenance easier.
Cons of Paddle Blenders:
- Gentle action may require more time to achieve a thorough mix than ribbon blenders.
- Generally bulkier, requiring more floor space for the same capacity as a ribbon blender.
- Mixing heavier or sticky materials may demand more energy and robust motors.
- May be more expensive because of their versatility and specialized capabilities.
Ribbon Blender vs Paddle Blender: What to Look for When Choosing
Must-Have Features for Your Ribbon Blender Purchase
- Look for blenders with well-designed inner and outer ribbons for efficient counter-flow mixing.
- Verify that the ribbon agitator is designed to minimize dead spots.
- Check if the gap between the ribbons and the trough wall is reasonable.
- Choose a stainless steel build, which is preferred for most applications.
- Ensure the trough has a smooth, polished finish to minimize material buildup and make cleaning easier.
- Choose a blender with variable speed controls for different mixing needs.
- Choose a valve that allows for quick and complete discharge of your materials.
- If you need to add minor liquids, look for blenders equipped with spray nozzles or ports.
- For temperature-sensitive processes, a jacketed trough can regulate material temperature.
Key Features to Look for in a Paddle Blender
- Paddles may be flat, curved, or have a special profile to suit specific materials.
- Ensure the paddle design allows for gentle yet thorough mixing.
- Stainless steel is the preferred construction material.
- Ensure all mixing components have a polished finish to aid in cleaning and reduce material adherence.
- Confirm the motor is robust enough to handle heavier or sticky materials.
- Some paddle blenders offer quick discharge through full-length doors, reducing unloading time.
- Integrated spray bars or injection ports facilitate the even distribution of liquids.
- Heating or cooling jackets are useful for processes requiring temperature control during mixing.
- Large doors or removable paddles simplify cleaning.
To Sum It All Up
So, these are the key differences between a ribbon blender and a paddle blender. If you want to handle a large volume of dry powders at a higher speed, a ribbon blender is a solid choice. And if you're handling fragile or sticky materials, a paddle blender might be the better option.
Remember to think about their differences when making your decision. The right blender can save you both money and time in the long run. Feel free to reach out if you're still unsure. We're here to help you find the perfect blender for your business!