When making medicine, you need reliable packaging to keep it sealed well and effective. There are many types of packging, such as bottles, blister packs, etc. The packaging includes everything from the small bottles and blister packs to the large boxes. Various types are suitable for holding different sizes of capsules or pills. They can protect the medicine from moisture, light, oxygen, and temperature changes.
Also, the packaging can help prevent contamination to keep the medicine effective. If you want to run a good medicine business, a thorough understanding of pharma packaging is a must.
Three Functional Pharma Packaging Types
Pharma packing can be divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging. Each of them has different functions and packaging methods.
Primary Packaging

Primary packaging directly contacts with the pharmaceutical products. It aims to offer a strict sealing condition. Common types include blister packs, bottles, vials, pouches, etc. Therefore, you should carefully select the material for this packaging type. Because it has a direct impact on the safety, and efficacy of the medicine. Importantly, you should ensure that the packaging material does not react with the medicine, which could alter its properties.
Secondary Packaging

Secondary packaging doesn’t have direct contact with medicine. It is mainly used to protect the primary packaging. So the whole protection for medicine could be stronger. Cartons and boxes are popular secondary packaging types. Manufacturers always put important information about the product on this packing type. It mainly includes instructions for use, expiration dates, and regulatory information.
Tertiary Packaging

Tertiary packaging is outside the secondary packaging. It is used for bulk handling, storage, and transportation of pharmaceutical products. So it needs great durability and strength to prevent goods from physical damage during shipping. They mainly includes corrugated cardboard boxes, crates, etc.
Six Common Materials for Pharma Packaging
Glass
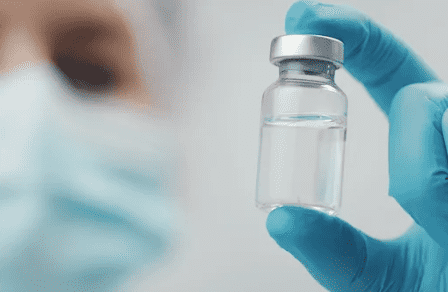
Glass is the most popular packing material in the healthcare industry. It is always used as primary packaging to directly contain and protect the medicine. This material does not react with the medicine inside, making it safe for storing sensitive drugs. Many manufacturers choose glass containers to place pills or liquid.
However, glass can break easily. So it usually needs additional protection during shipping, such as adding more foams. And glass is heavier than other materials. It increases shipping costs.
Plastic
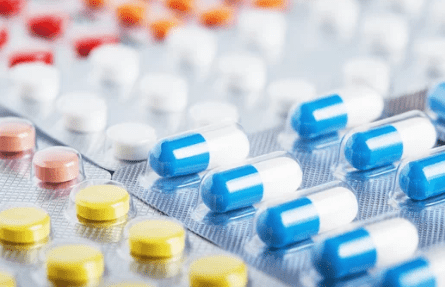
Plastic is widely used in pharma packaging. It features lightweight, durability and good strength. Plastic has different types to choose from and could be used for various functions.
- PE. It is known for its good chemical inertness and moisture resistance. PE does not react with most drugs, ensuring drug stability. It is mainly used for making medicine bottles, syrup bottles, and bottle caps.
- PP. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heat-sterilized drug packaging, like syringes. PP has excellent resistance to acids, bases, and most chemicals. So it is very suitable for ampoules and tablet bottles.
- PVC. It features high transparency, allowing direct observation of the drug’s condition and quantity. Good forming properties make it easy to shape into various forms. It is always used for blister packs and infusion bags. During production, you can also add plasticizers to adjust flexibility and hardness.
- PET. It offers strong strength and rigidity, protecting contents from physical damage. It is often used for transparent medicine bottles, such as vitamins or liquid supplements. However, PET has higher production costs compared to other plastics.
These are some commonly used packaging plastics in the medical industry. You can choose the most suitable one based on your production needs. Please note that some plastics may react with certain drugs, so careful consideration is a must.
Aluminum
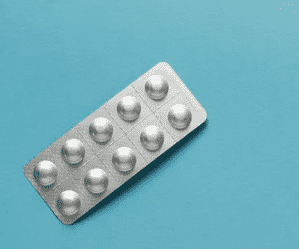
When referring to metal packaging materials, Aluminum is a good choice. It has excellent protection against light, moisture, and air. It is also resistant to physical damage and punctures. Aluminum is always used in primary packaging to provide a strong, protective barrier. Many tubes and foils are made of this material. For example, many backboards of blister packs are made of Aluminum.
Rubber

Rubber is commonly used for stoppers and closures in vials and bottles. It creates a tight seal, preventing contamination and leaks. But rubber can degrade over time, especially when exposed to certain chemicals.
Paper
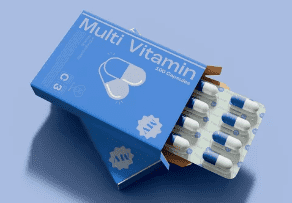
Paper is commonly used in secondary pharmaceutical packaging, such as cartons and boxes. They can encase primary packaging like bottles or blister packs. The advantages of the paper include its lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and ease of printing. Additionally, paper is biodegradable and recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
However, paper offers limited protection against moisture and physical damage. In real business, many suppliers choose to apply another moisture-resistant coating to the surface of the carton. It can enhance the protective qualities of the paper carton.
Wood

Wood is less commonly used in pharmaceutical packaging. It is mainly used in tertiary packaging, such as crates or pallets for bulk transportation. The strengths of wood include its robustness, durability, and ability to support heavy loads. So it is suitable for protecting large shipments during transit.
However, it has limitations. Wood is sensitive to moisture, which can lead to mold and degradation. So it needs special treatments to ensure safety, such as chemical treatments.
Three Considerations when Choosing Medical Packaging Materials
When choosing materials for pharmaceutical packaging, several important factors must be considered to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of the medication. Here are three key criteria for your reference.
Drug Properties
External factors are some of the most significant influences on drug efficacy, such as light and moisture. Different medicines have various properties. Therefore, they require different materials to maintain stability and effectiveness. For instance, some drugs are particularly sensitive to moisture. So they need packaging materials with a strong moisture barrier, such as aluminum foil.
Drug Compatibility
It means that the packaging material should not react chemically with the drug. If the packaging material interacts with the medicine, it could change the drug's properties. This makes the drug less effective or even harmful. For example, certain plastics might absorb components of the drug or release harmful substances into it. Then the whole drug will be useless and you will get a loss.
Ease Processing
It refers to how easily the packaging can be produced, filled, sealed, and shipped. The packaging process should be efficient and not require complex machinery or processes. Otherwise, you would get a slower production time or increased costs.
The packaging should also be easy to handle for both manufacturers and consumers. For example, blister packs are often chosen for tablets. Because they are not only easy to manufacture, but also lightweight, and convenient for consumers to use.
The End
Various packaging materials suit different medical needs. Each of them has pros and cons. You should consider key properties to ensure safe and effective packaging.
At Huada Pharma, we have a series of pharmaceutical machinery to meet your needs. They are designed to handle a wide range of work and packaging materials. Whether you need blister packing machines, tablet presses, or capsule filling machines, Huada Pharma offers solutions that meet the highest industry standards. Don’t hesitate to contact us and upgrade your business.